Overview of GLP-1 Medications for Weight-Loss
Using GLP-1 medications for weight loss has become popular over the past few years. The effectiveness of these drugs and compelling data behind their mechanism of action made them very popular among those looking to lose weight.
Taking “diet pills” or other medication that isn’t approved by the FDA can lead to dire consequences. Luckily, there are safe alternatives. GLP-1 medications are medication used to control blood sugar in individuals with type II diabetes. However, some GLP-1 medications have been approved by the FDA to help people lose weight.
In this article, we will cover several GLP-1 medications to see how they promote weight loss. Only evidence-based, peer-reviewed, sources will be sited.
What are GLP-1 medications?
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) medications are commonly prescribed to treat type II diabetes. These drugs are very effective at reducing blood glucose levels. Researchers also found that GLP-1 medications improve cardiovascular and renal health, and can help patient’s lose weight.
There are several types of these medications on the market. Albeit they affect the body similarly, there are a few notable differences.
The primary factor that differentiates each medication from one another is their half-life (i.e., how long they stay in your body). Half-lives can be broken down into two sub-types: short-acting and long-acting.
Short-acting GLP-1 Medications
Short-acting GLP-1 medications have a half-life of around one day. This makes them ideal for post-meal sugar control.
There are three short-acting GLP-1 medications approved in the United States:
- Exenatide (Byetta)
- Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)
- Oral semaglutide (Rybelsus)
Long-acting GLP-1 Medication List
Long-acting GLP-1 medications have a half-life that could reach up to seven days.
There are four long-acting GLP-1 medications approved in the United States:
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
- Exenatide extended-release (Bydureon)
- Liraglutide (Victoza)
- Semaglutide (Ozempic)
The difference between these two classes is how often you have to take them. Medications like Rybelsus and Saxenda must be taken everyday because they have a half-life of ~1 day. On the other hand, medications like Ozempic are taken every week, because they have a half-life of about 7 days.
How do GLP-1 medications cause weight loss
GLP-1 medications target several metabolic pathways to lower blood sugar levels. These same pathways can promote weight loss.
These mechanisms include…
- Slowing down gastric emptying – Slowing down digestion will directly prevent post-meal glucose spikes. Glucose and insulin spikes are strongly correlated to weight gain, as supported here. plenty of research
- Inducing satiety – GLP-1 medications seem to induce feelings of fullness rapidly after food ingestion. Decreased appetite is imperative to stopping food cravings and promoting weight loss.
- Increasing insulin production – GLP-1 might help the pancreas secrete more insulin. This is helpful because insulin overweight and obese individuals often suffer from insulin resistance, leading to obesity.
- Preventing gluconeogenesis – Gluconeogenesis is the process of making new glucose molecules by hepatocytes (i.e., liver cells). Limiting the rate of this reaction stops future weight gain.
How to take GLP-1 medications for weight loss?
In general, you need to inject GLP-1 medications subcutaneously–which means into body fat. The one exception to this role is oral semaglutide, which is known in the US as Rybelsus.
You will find these medications are packaged as disposable pen injection devices. These devices cause minimal discomfort during injection due to the small needle tip.
Some pens come with predetermined doses for single use only, while other devices allow you to select the desired dosage.
Similar to insulin injections, you can inject GLP-1 medications in your:
- Stomach
- Thighs
- Upper arm
GLP-1 Medications and Weight-Loss
The mechanisms we covered above all contribute to the weight loss-promoting properties of GLP-1 medications.
Pharmaceutical companies like Novo Nordisk have produced GLP-1 agonists, which produce the same effect as GLP-1, but doesn’t get degraded immediately after injection. This means they can help you stay full, reduce your appetite, and positively affect your metabolism. Medications like liraglutide (Victoza) and semaglutide (Ozempic) are both FDA approved drugs that do this.
Compared to natural GLP-1 molecules produced by your body, these medications last much longer. Naturally produced GLP-1 last less than 2 minutes in the blood due to an enzyme called DPP4. DPP4 rapidly degrades GLP-1, leaving many patients feeling as if they have an insatiable appetite. These medications work to reduce your appetite, increase insulin producing, and prevent gluconeogenesis, all leading to significant weight-loss.
The First GLP-1 Medication:
In 2015, the FDA approved the use of Saxenda (liraglutide) 3 mg for weight loss. Saxenda is the first GLP-1 drug approved for weight loss. Typically, patients need to take 0.6 mg of liraglutide once a day during the first week. Doctors then gradually increase the dose by 0.6 mg every week until the patient is at 3 mg / day.
Semaglutide, on the other hand, received FDA approval in June 2021. The initial dose is 0.25 mg per day. After that, your doctor will gradually titrate your dose upward. boosted until we reach 2.4 mg per day.
Ozempic V.S. Saxenda: 52-week Weight-Loss Analysis
The chart below demonstrates the degree of weight loss seen in patients who took Ozempic and Saxenda for 52 weeks:
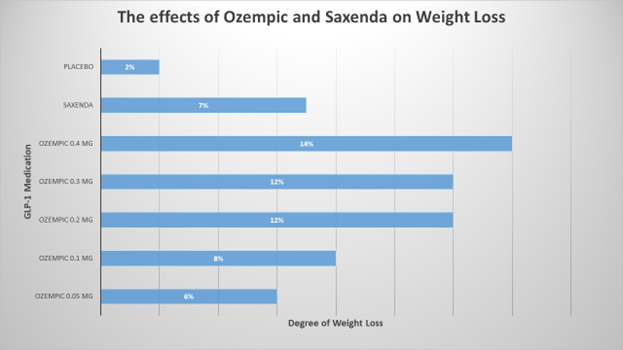
The data is from a large clinical trial that included 957 non-diabetic participants with weight issues. Patients taking Ozempic 0.4 mg for one year was enough to cause a 14% weight loss. In medical terms, doctors refer to this as clinically significant weight-loss.
Note that slow and steady weight loss is always preferable over rapid weight loss. According to one study, up to 95% of people who lose weight rapidly will gain it back within 12 months. Today, researchers advocate for slow but steady weight loss. Therefore, the 14% weight loss induced by Ozempic 0.4 mg is an excellent rate.
If you’re looking for an Ozempic prescription to help you lose weight, book an appointment with one of our online Providers. If we are unable to you aren’t prescribed Ozempic (or an alternative medication that your insurance covers), you’ll get 100% of your money back!
What’s Next?
Tirzepatide is the newest medication. It goes by the brand name Mounjaro. This drug received FDA approval in 2022 to treat type II diabetes. However, researchers noticed its significant effects on weight loss when conducting clinical trials. Participants lost 20% of their body weight.
Due to these incredible effects, regulators granted Mounjaro a fast-track designation to review it as a potential therapy for obesity.
If you have any health issues, make sure to speak with your primary care physician before taking medications for weight loss.
Takeaway message
GLP-1 medications are amazing drugs that help millions of diabetic patients all over the world. Recent evidence suggests that these medications can be useful in promoting weight loss. As a result, GLP-1 receptor agonists could play a preventive role, saving millions of people from cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
We hope that this article managed to highlight the role of GLP-1 medications in promoting weight loss and how we can use them in clinical practice.
If you have any questions or concerns about these medications, please do not hesitate to share your thoughts with us. You can also try GLP-1 assisted medical weight loss through Healthcare Intermediaries for just $79/month!